Convention plugins apply conventions to a build. They do this by applying ecosystem plugins such as AGP and KGP, and then configuring those plugins according to the convention used by your build.
In this tutorial, you will learn how you can migrate your project to use convention plugins in small and detailed steps. So let’s get started.
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Setting up build-logic project
- Start by creating the
build-logicfolder inside your root project.
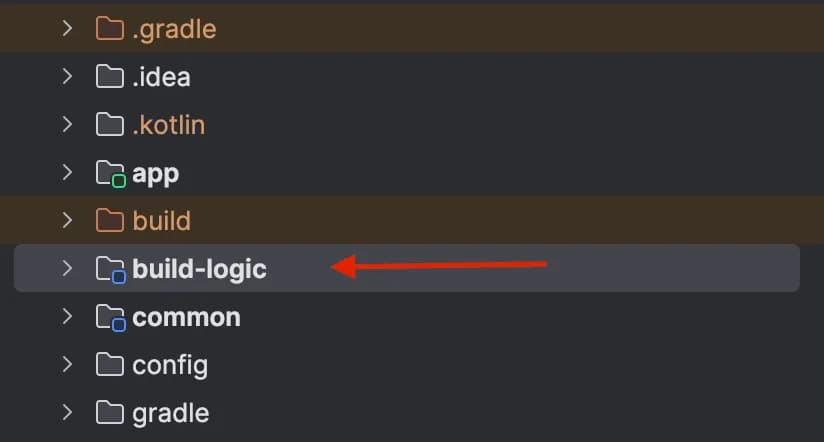
- Create a file named
settings.gradle.ktsinside thebuild-logicdirectory and add following configuration:
dependencyResolutionManagement {
// 1. Setup repositories to download dependencies
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
// 2. Create version catalog named `libs` from
// the `libs.versions.toml` file already present in
// the gradle folder.
versionCatalogs {
create("libs") {
from(files("../gradle/libs.versions.toml"))
}
}
}
// 3. Set project name
rootProject.name = "build-logic"
// 4. Include the `convention` module that we will create next
include(":convention")Here we have setup basic configuration for the build-logic project. This tutorial assumes that your project is using version catalog.
- Create a
gradle.propertiesfile and add the following properties:
org.gradle.parallel=true
org.gradle.caching=true
org.gradle.configureondemand=true- Add
build-logicas an included build in your<root>/settings.gradle.kts:
pluginManagement {
// 1. Add build-logic as an includedBuild
includeBuild("build-logic")
repositories {
google {
content {
includeGroupByRegex("com\\.android.*")
includeGroupByRegex("com\\.google.*")
includeGroupByRegex("androidx.*")
}
}
mavenCentral()
gradlePluginPortal()
}
}Setting up convention module
- Start by creating a directory called
conventionin yourbuild-logicdirectory:
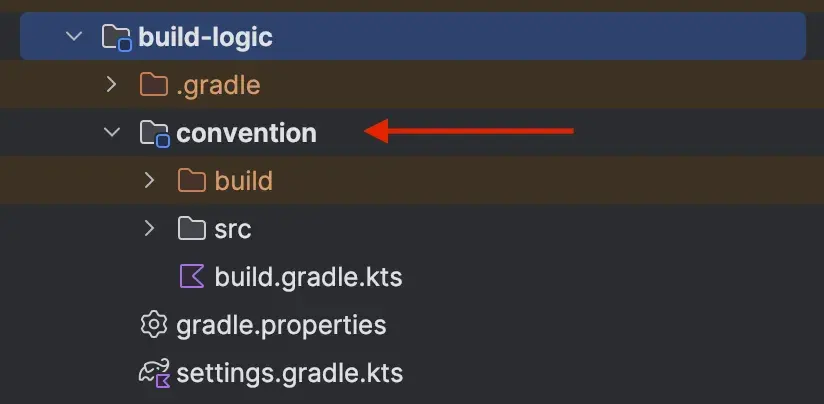
- Create a
build.gradle.ktsinside theconventiondirectory and add basic configuration:
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.JvmTarget
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
// Note: Replace with your package name
group = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.buildlogic"
// Configure the build-logic plugins to target JDK 17
// This matches the JDK used to build the project, and is not related to what is running on device.
java {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
}
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
jvmTarget = JvmTarget.JVM_17
}
}
tasks {
validatePlugins {
enableStricterValidation = true
failOnWarning = true
}
}- Next we will add plugins to the version catalog that are required by the
build-logic. Add these plugins togradle/libs.versions.tomlfile:
[versions]
# ...
agp = "8.4.2"
androidTools = "31.4.2"
kotlin = "2.0.0"
[libraries]
# ...
# Dependencies of the included build-logic
android-gradlePlugin = { group = "com.android.tools.build", name = "gradle", version.ref = "agp" }
android-tools-common = { group = "com.android.tools", name = "common", version.ref = "androidTools" }
compose-gradlePlugin = { module = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:compose-compiler-gradle-plugin", version.ref = "kotlin" }
kotlin-gradlePlugin = { group = "org.jetbrains.kotlin", name = "kotlin-gradle-plugin", version.ref = "kotlin" }- Now apply these plugins in your
build-logic/convention/build.gradle.ktsfile:
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.JvmTarget
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
// Note: Replace with your package name
group = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.buildlogic"
// Configure the build-logic plugins to target JDK 17
// This matches the JDK used to build the project, and is not related to what is running on device.
java {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
}
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
jvmTarget = JvmTarget.JVM_17
}
}
tasks {
validatePlugins {
enableStricterValidation = true
failOnWarning = true
}
}
// 1.Add plugins here
dependencies {
compileOnly(libs.android.gradlePlugin)
compileOnly(libs.android.tools.common)
compileOnly(libs.compose.gradlePlugin)
compileOnly(libs.kotlin.gradlePlugin)
}- Next create the source set directory inside
conventionmodule:
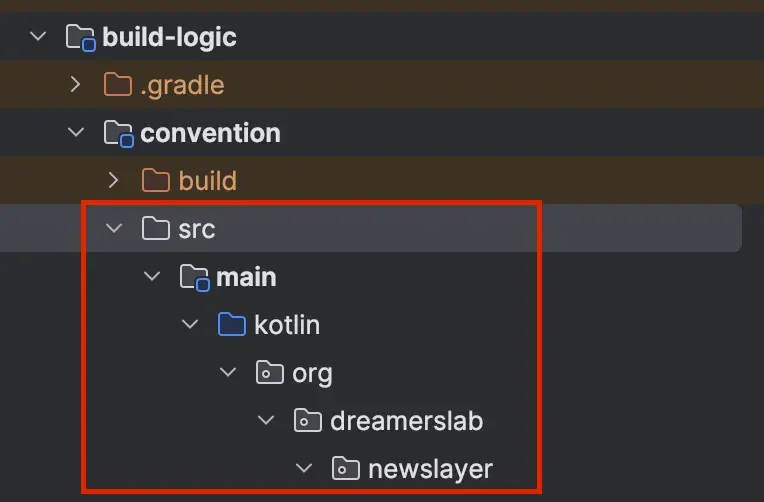
Creating configuration helper files
Let’s create the helper files that we will use to configure different plugins. We start by creating a file for project extensions:
ProjectExtensions.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.api.artifacts.VersionCatalog
import org.gradle.api.artifacts.VersionCatalogsExtension
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.getByType
val Project.libs
get(): VersionCatalog = extensions.getByType<VersionCatalogsExtension>().named("libs")Versions.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
object Versions {
const val COMPILE_SDK = 34
const val MIN_SDK = 24
const val TARGET_SDK = 34
}KotlinAndroid.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.api.dsl.CommonExtension
import org.gradle.api.JavaVersion
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.api.plugins.JavaPluginExtension
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.assign
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.configure
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.provideDelegate
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.JvmTarget
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.KotlinAndroidProjectExtension
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.KotlinJvmProjectExtension
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.KotlinTopLevelExtension
/**
* Configure base Kotlin with Android options
*/
internal fun Project.configureKotlinAndroid(
commonExtension: CommonExtension<*, *, *, *, *, *>,
) {
commonExtension.apply {
compileSdk = Versions.COMPILE_SDK
defaultConfig {
minSdk = Versions.MIN_SDK
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
}
}
configureKotlin<KotlinAndroidProjectExtension>()
}
/**
* Configure base Kotlin options
*/
private inline fun <reified T : KotlinTopLevelExtension> Project.configureKotlin() = configure<T> {
// Treat all Kotlin warnings as errors (disabled by default)
// Override by setting warningsAsErrors=true in your ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
val warningsAsErrors: String? by project
when (this) {
is KotlinAndroidProjectExtension -> compilerOptions
is KotlinJvmProjectExtension -> compilerOptions
else -> TODO("Unsupported project extension $this ${T::class}")
}.apply {
jvmTarget = JvmTarget.JVM_11
allWarningsAsErrors = warningsAsErrors.toBoolean()
freeCompilerArgs.add(
// Enable experimental coroutines APIs, including Flow
"-opt-in=kotlinx.coroutines.ExperimentalCoroutinesApi",
)
}
}AndroidCompose.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.api.dsl.CommonExtension
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.assign
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.configure
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.dependencies
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.compose.compiler.gradle.ComposeCompilerGradlePluginExtension
/**
* Configure Compose-specific options
*/
internal fun Project.configureAndroidCompose(
commonExtension: CommonExtension<*, *, *, *, *, *>,
) {
commonExtension.apply {
buildFeatures {
compose = true
}
dependencies {
val bom = libs.findLibrary("androidx-compose-bom").get()
add("implementation", platform(bom))
add("androidTestImplementation", platform(bom))
add("implementation", libs.findLibrary("androidx-ui-tooling-preview").get())
add("debugImplementation", libs.findLibrary("androidx-ui-tooling").get())
}
}
extensions.configure<ComposeCompilerGradlePluginExtension> {
enableStrongSkippingMode = true
}
}Creating plugins
We will create following necessary plugins:
| Plugin | Usage |
|---|---|
| AndroidApplicationConventionPlugin | Configures base application |
| AndroidApplicationComposeConventionPlugin | Adds configuration for Compose to application module |
| AndroidLibraryConventionPlugin | Configures android library modules |
| AndroidLibraryComposeConventionPlugin | Adds configuration for Compose to android library modules |
Let’s create these plugins:
AndroidApplicationConventionPlugin.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.api.dsl.ApplicationExtensio
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.configure
class AndroidApplicationConventionPlugin : Plugin<Project> {
override fun apply(target: Project) {
with(target) {
with(pluginManager) {
apply("com.android.application")
apply("org.jetbrains.kotlin.android")
}
extensions.configure<ApplicationExtension> {
configureKotlinAndroid(this)
defaultConfig.targetSdk = Versions.TARGET_SDK
}
}
}
}AndroidApplicationComposeConventionPlugin.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.api.dsl.ApplicationExtension
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.apply
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.getByType
class AndroidApplicationComposeConventionPlugin : Plugin<Project> {
override fun apply(target: Project) {
with(target) {
apply(plugin = "com.android.application")
apply(plugin = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.compose")
val extension = extensions.getByType<ApplicationExtension>()
configureAndroidCompose(extension)
}
}
}AndroidLibraryConventionPlugin.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.gradle.LibraryExtension
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.apply
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.configure
class AndroidLibraryConventionPlugin : Plugin<Project> {
override fun apply(target: Project) {
with(target) {
with(pluginManager) {
apply("com.android.library")
apply("org.jetbrains.kotlin.android")
}
extensions.configure<LibraryExtension> {
configureKotlinAndroid(this)
defaultConfig.targetSdk = Versions.TARGET_SD
}
}
}
}AndroidLibraryComposeConventionPlugin.kt
package org.dreamerslab.newslayer
import com.android.build.gradle.LibraryExtension
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.apply
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.getByType
class AndroidLibraryComposeConventionPlugin : Plugin<Project> {
override fun apply(target: Project) {
with(target) {
apply(plugin = "com.android.library")
apply(plugin = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.compose")
val extension = extensions.getByType<LibraryExtension>()
configureAndroidCompose(extension)
}
}
}Register plugins
Once you have created the plugins, you need to register them in build-logic/convention/build.gradle.kts :
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.JvmTarget
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
group = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.buildlogic"
// Configure the build-logic plugins to target JDK 17
// This matches the JDK used to build the project, and is not related to what is running on device.
java {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
}
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
jvmTarget = JvmTarget.JVM_17
}
}
tasks {
validatePlugins {
enableStricterValidation = true
failOnWarning = true
}
}
dependencies {
compileOnly(libs.android.gradlePlugin)
compileOnly(libs.android.tools.common)
compileOnly(libs.compose.gradlePlugin)
compileOnly(libs.kotlin.gradlePlugin)
}
// 1. Register your plugins here
gradlePlugin {
plugins {
register("androidApplicationCompose") {
id = "newslayer.android.application.compose"
implementationClass = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.AndroidApplicationComposeConventionPlugin"
}
register("androidApplication") {
id = "newslayer.android.application"
implementationClass = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.AndroidApplicationConventionPlugin"
}
register("androidLibraryCompose") {
id = "newslayer.android.library.compose"
implementationClass = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.AndroidLibraryComposeConventionPlugin"
}
register("androidLibrary") {
id = "newslayer.android.library"
implementationClass = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.AndroidLibraryConventionPlugin"
}
}
}When registering a plugin, we pass its name, a unique id and the implementationClass . We will later use the id to apply these plugins in our modules just like we apply an external plugin using its id.
Add custom plugins to version catalog
We can now add these plugins inside our gradle/libs.versions.toml file:
[plugins]
# ...
# Plugins defined by this project
newslayer-android-application = { id = "newslayer.android.application", version = "unspecified" }
newslayer-android-application-compose = { id = "newslayer.android.application.compose", version = "unspecified" }
newslayer-android-library = { id = "newslayer.android.library", version = "unspecified" }
newslayer-android-library-compose = { id = "newslayer.android.library.compose", version = "unspecified" }Applying plugins in our project
We have successfully created custom plugins that we can now apply to our project modules. We will start by migrating the app module. Update the build gradle file as follows:
app/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.android.application)~~
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.jetbrains.kotlin.android)~~
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.compose.compiler)~~
// Apply custom plugins here
alias(libs.plugins.newslayer.android.application)
alias(libs.plugins.newslayer.android.application.compose)
}
android {
namespace = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer"
// ~~compileSdk = 34~~
defaultConfig {
applicationId = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer"
// ~~minSdk = 24~~
// ~~targetSdk = 34~~
versionCode = 1
versionName = "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
vectorDrawables {
useSupportLibrary = true
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
isMinifyEnabled = true
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro",
)
}
}
// ~~compileOptions {~~
// ~~sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17~~
// ~~targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17~~
// }
// ~~kotlin {~~
// ~~jvmToolchain(17)~~
// ~~}~~
// ~~buildFeatures {~~
// ~~compose = true~~
// ~~}~~
packaging {
resources {
excludes += "/META-INF/{AL2.0,LGPL2.1}"
}
}
}
dependencies {
// ...
// ~~implementation(platform(libs.androidx.compose.bom))~~
// ~~implementation(libs.androidx.ui.tooling.preview)~~
// ~~androidTestImplementation(platform(libs.androidx.compose.bom))~~
// ~~debugImplementation(libs.androidx.ui.tooling)~~
}We will also apply custom plugins to out android modules that use compose. I’ll apply it to the. :common:ui module.
common/ui/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.android.library)~~
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.jetbrains.kotlin.android)~~
// ~~alias(libs.plugins.compose.compiler)~~
// Apply plugins
alias(libs.plugins.newslayer.android.library)
alias(libs.plugins.newslayer.android.library.compose)
}
android {
namespace = "org.dreamerslab.newslayer.ui"
// ~~compileSdk = 34~~
defaultConfig {
// ~~minSdk = 24~~
testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
consumerProguardFiles("consumer-rules.pro")
}
// ~~compileOptions {~~
// ~~sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17~~
// ~~targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17~~
// ~~}~~
// ~~kotlin {~~
// ~~jvmToolchain(17)~~
// ~~}~~
// ~~buildFeatures {~~
// ~~compose = true~~
// ~~}~~
}
dependencies {
// ...
// ~~implementation(platform(libs.androidx.compose.bom))~~
// ~~implementation(libs.androidx.ui.tooling.preview)~~
// ~~androidTestImplementation(platform(libs.androidx.compose.bom))~~
// ~~debugImplementation(libs.androidx.ui.tooling)~~
}By following this approach, you can update your sub-modules to use build-logic plugins.
Enable caching for faster builds
Add following properties to your <root>/gradle.properties to enable caching for faster builds:
# Enable caching between builds.
org.gradle.caching=true
# Enable configuration caching between builds.
org.gradle.configuration-cache=true